News
Exploring Backup Power in Data Centers
Having backup power in a data center is an absolute must. Think of data centers as highly specialized facilities with networked computers, storage systems, and servers that all work together to support an organization’s data-driven tasks. Multiple organizations count on a single data center to provide them with the secure information they need to keep operations up and running. With so much on the line, making sure that this vital information stays safe is a data center’s number one priority.
A sudden power interruption can mean serious consequences for a data center. If the power goes out, even for just a few minutes, it can cause data to be corrupted, leaked, or lost altogether. That’s why effective power distribution and a backup power system are non-negotiable. In this blog, we’ll look at some of the key players in a data center’s power distribution infrastructure and explore the reasons why having a backup power system is so important.
How Backup Power Works in Data Centers
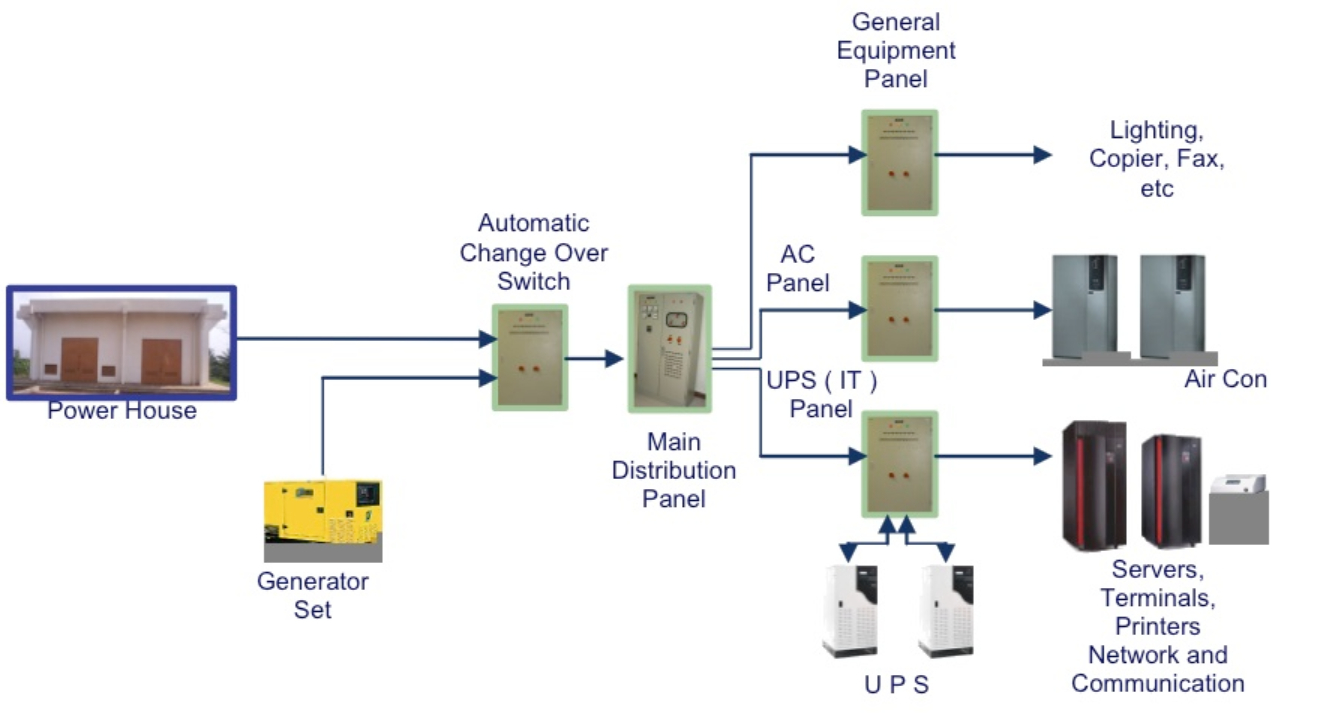
Like your home, data centers are connected to utility power and use the electrical grid as its main power source. During a power outage, a data center’s backup power system relies on a transfer switch, generator, and a UPS system (uninterrupted power supply system) to ensure that its power supply doesn’t fail. Transfer switches are tasked with shifting the data center from utility power to running off its backup power source, while a UPS system provides emergency power until the electric grid can be restored or the data system has time to safely shut down.
A UPS system uses batteries to store electricity and save it for later use. While they’re a great option to support a steady supply of electricity, they only provide enough power to keep operations running for an additional 30 minutes. So, it’s ideal for data centers to use a combination of a UPS system and a standby generator to continue functioning during a blackout.
Both utility and backup power infrastructures use cooling and PUE systems to keep electrical networks running to the best of their abilities. Cooling systems use a combination of liquid cooling and precision air conditioning to keep power equipment from overheating. PUE systems, also known as power monitoring and management systems, monitor the energy consumption of the power system and provide feedback that can be used to maximize efficiency and reduce costs.
The Role of PDUs (Power Distribution Units)
Just like its name implies, power distribution units (PDUs) move electricity from the data center’s utility or backup power source to downstream equipment. PDUs come in different variations such as basic, metered, monitored, and switched. Basic PDUs are the simplest of these variations and are designed to distribute electricity without any bells or whistles. Metered PDUs are a bit more advanced than basic PDUs, because they track the amount of electricity being used and provide data center personnel with valuable feedback.
Monitored PDUs measure and monitor electrical currents to send out alerts if anything looks unusual. Finally, switched PDUs offer users with the most flexibility and control of all these variations, because they allow the power system to be remote-controlled. The type of PDU used in a data center depends on the level of control and monitoring required for each application.
Busway systems are a fairly new style of PDU setup that’s often used in large-scale electrical systems. They use busbars in a protective enclosure, alongside fittings and other accessories to transport electrical currents throughout the data center. Busway systems have a modular design, which means that the entire system is made of smaller components that can be taken apart and recombined to create new structures. This leaves plenty of room for scalability so that the data center’s power distribution system can be expanded as its needs change over time.
Rack Power Distribution Units (rack-mounted PDUs) are the final destination in a PDU chain. These units gather electricity from upstream PDU equipment and allocate a precise amount of power to each piece of IT equipment. Its strength lies in its ability to cater to a diverse range of power needs. They can support a variety of outlets and sometimes include features such as metering, remote monitoring, and power management abilities.
Power Solutions for Data Centers
We offer a wide range of innovative power solutions in a diverse range of configurations. Our CCBs (Camlock Connection Boxes) and Cable Assemblies are engineered to provide reliable power distribution to keep operations moving. Its industry-standard Series 16 Camlocks quickly connect with our Cable Assemblies and Pigtails for hassle-free installation. This powerful combination is perfect for offering your customers the reliability and scalability their data center needs.
In addition to our Camlock Connection Box and Cable Assemblies, our LBS (Load Bank Docking Stations), GDS (Generator Docking Station), and TruOne Dual-Voltage ATS (Automatic Transfer Switches) are excellent for supporting backup power in a data center. In a data center’s PDU chain, this equipment ties into the standby or portable generator to support effective power distribution and a continuous stream of electricity.
If you commonly work in the data center industry and require effective power solutions, please contact our distributor relations team at [email protected] or call (866)-825-8525. We’ll be happy to connect you with one of our talented team members and help you provide your customers with the power solutions they need to succeed. Click below to download our free data center presentation.

